What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin, introduced in 2009, represents a groundbreaking shift in the realm of digital money. Created by the pseudonymous figure Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin emerged as the first decentralized cryptocurrency, setting a precedent for the evolution of digital currencies. Unlike traditional forms of currency, which are regulated by central authorities and governments, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network known as blockchain technology. This decentralized nature allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries such as banks, thus challenging conventional financial systems.
The fundamental technology behind Bitcoin, the blockchain, is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. Each transaction is verified by network nodes through cryptography and is grouped into blocks, which are then linked together to form a chain. This structure not only ensures the integrity and security of transactions but also provides transparency, as all participants within the network have access to the same transactional data.
Bitcoin has gained significant traction since its inception, evolving from a niche digital asset to a widely recognized form of currency accepted by various merchants and platforms. The appeal of Bitcoin lies in its limited supply, which stands at 21 million coins, making it a deflationary currency. This aspect, coupled with increasing adoption in trading and investment circles, has propelled Bitcoin’s price and popularity within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
As individuals and businesses continue to explore the possibilities offered by digital money, Bitcoin remains at the forefront of discussions about the future of finance. Its innovations have inspired countless other cryptocurrencies, establishing a burgeoning sector of digital assets traded across various exchanges. Understanding Bitcoin serves as essential knowledge within the broader narrative of the digital currency revolution.
How Bitcoin Works: The Blockchain Technology
Bitcoin operates on a revolutionary technology known as blockchain, which serves as the backbone of the entire ecosystem. Essentially, a blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger that records all transactions made with Bitcoin. This ledger is maintained across a network of computers, often referred to as nodes, which work collaboratively to validate and secure each transaction. Unlike traditional banking systems that rely on a central authority to oversee transactions, blockchain utilizes cryptographic techniques to ensure the integrity and security of data.
Every transaction involving Bitcoin is grouped into a block and subsequently added to a chain of previous transactions, forming a chronological sequence. This chronological chain is immutable, meaning once a block is added, it cannot be altered or deleted. Each new block contains a unique cryptographic hash of the preceding block, creating a secure link between them. This mechanism not only ensures transparency but also mitigates the risk of fraud and double-spending, a common concern in digital money transactions.
The decentralized nature of blockchain technology is distinctive, as it eliminates reliance on a single governing entity. Instead, the control is spread across the network, allowing users to have more autonomy over their transactions. When a user initiates a Bitcoin transaction, it is broadcast to the entire network, where miners validate it. These miners use their computational power to solve complex mathematical problems, thereby confirming and adding transactions to the blockchain. In return for this effort, miners are rewarded with newly created Bitcoin, incentivizing them to maintain the network’s security and efficiency.
With this decentralized and secure structure, blockchain technology provides a reliable environment for trading and storing Bitcoin. Its ability to offer transparent and tamper-proof records positions Bitcoin and its blockchain at the forefront of the financial revolution, leveraging the advantages of digital money while addressing many challenges associated with traditional exchanges and banking systems.
The Value Proposition: Why Bitcoin Matters
Bitcoin has emerged as a pivotal player in the realm of digital money, showcasing diverse use cases that extend far beyond mere transactions. One of the most compelling applications of Bitcoin is its role in facilitating online transactions. With its decentralized nature, Bitcoin allows users to send and receive payments directly, bypassing traditional banking systems and reducing transaction fees. This feature is particularly advantageous for businesses and consumers alike in an increasingly digital world.
In addition to online transactions, Bitcoin is also utilized for international remittances. Traditional money transfers can involve high fees and long processing times, creating barriers for individuals and families reliant on cross-border payments. Bitcoin provides an efficient alternative, allowing users to send funds quickly and at a fraction of the cost. This capability fosters financial inclusion, especially in regions where access to banking is limited.
Moreover, Bitcoin has garnered significant attention as an investment vehicle. Many investors view this cryptocurrency as a hedge against inflation, akin to gold, due to its capped supply of 21 million coins. This scarcity introduces a concept known as deflationary economics, where the value of Bitcoin may appreciate as demand increases while supply remains static. As a result, investors are increasingly looking to Bitcoin not just as a digital currency but as a store of value, mitigating risks associated with financial instability.
In essence, Bitcoin represents a substantial innovation in the financial landscape, offering a decentralized alternative to conventional currencies. Its applications in online transactions, remittances, and as a store of value help to underline its significance as a form of cryptocurrency and digital money that could redefine the future of trading and investment.
The Volatility of Bitcoin: Risks and Rewards
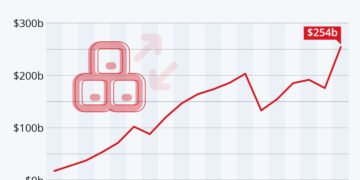
The market dynamics governing Bitcoin, a leading form of cryptocurrency, are predominantly influenced by the principles of supply and demand. Since its inception, Bitcoin has exhibited remarkable price volatility, with its value experiencing substantial ups and downs. This characteristic is not only reflective of investor sentiment but also highlights the immature state of the market relative to other forms of currency. Specific events, such as regulatory news or technological advancements, often lead to sharp price movements, presenting both risks and rewards for investors.
Historically, Bitcoin’s price has undergone extreme fluctuations. For instance, in late 2017, Bitcoin soared to nearly $20,000, only to plunge to around $3,000 a year later. Such volatility can be disconcerting; however, it also offers trading opportunities for those looking to capitalize on market movements. Investors who understand the underlying factors affecting Bitcoin, including trading volumes on various exchanges and global economic conditions, may find ways to mitigate risks while reaping potential rewards.
In assessing the investment opportunity posed by Bitcoin, it is essential to weigh both its promising rewards against the inherent risks. Understanding the influences on this cryptocurrency market is crucial for informed decision-making and proactive risk management.
At Light House Streak, we streak the lines.